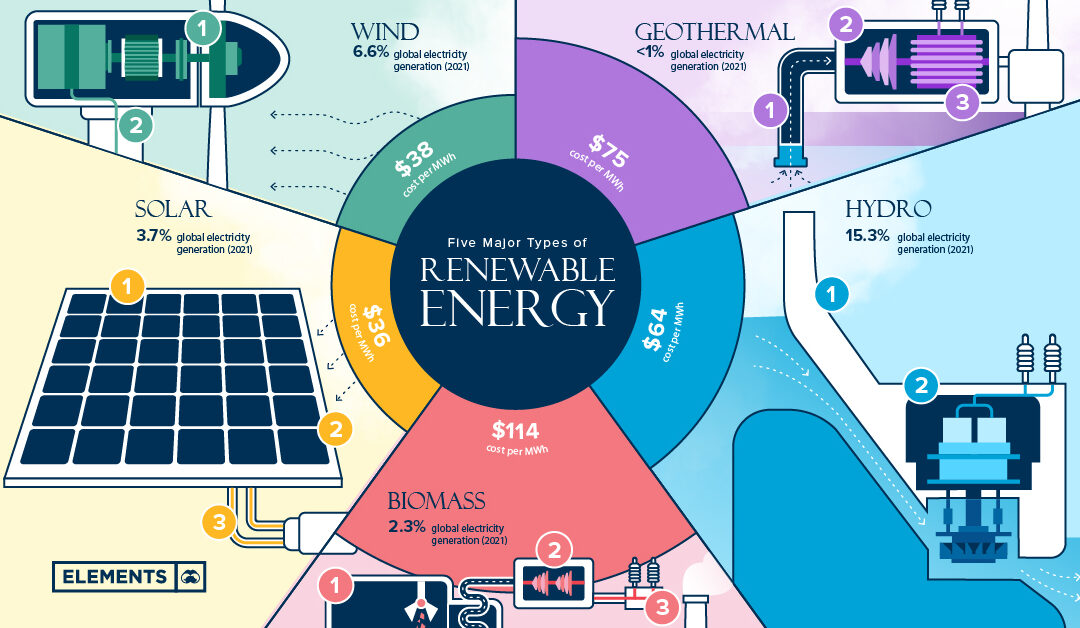
In a world hungry for sustainable solutions, a remarkable surge in renewable energy capacity provides a glimmer of hope. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reported a 9.6 percent increase in global renewable energy capacity in 2022. As wind and solar power, which account for 90 percent of the net additions, take center stage, the remarkable growth is a testament to the ongoing shift toward clean energy.
While these strides are commendable, it is vital to recognize that much more needs to be done to ensure a sustainable future for our planet. Let’s explore recent highlights in the global renewable energy landscape, the increasing significance of carbon allowance sales, and recent developments shaping the energy transition worldwide.
The Global Rise of Renewable Energy Capacity
The surge in renewable energy capacity has propelled the world toward a greener future. In 2022 the total global renewable energy capacity reached an impressive 3,372 gigawatts (GW), marking an increase of 295 GW compared to the previous year. China emerged as the frontrunner, contributing 141 GW, with wind and solar power installations dominating the landscape. Europe and North America also witnessed substantial growth; renewables in these regions grew by 57.3 GW and 29.1 GW, respectively. In an unexpected turn of events, the Middle East recorded its highest increase in renewables on record, commissioning 3.2 GW of new capacity, representing a remarkable 12.8 percent increase from the previous year.
While these figures highlight the resilience of renewable energy in the face of persistent energy crises, it is crucial to acknowledge that annual additions of renewable power capacity must triple the current level by 2030. This accelerated growth is necessary to stay on track with the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
The Increasing Significance of Carbon Allowance Sales
Governments worldwide are recognizing the urgency of combating pollution and leveraging carbon allowance sales to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon future. Sales of carbon allowances generated an unprecedented $63 billion in 2022, marking a $4 billion increase from the previous year. This tremendous achievement underscores the growing commitment of governments worldwide to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Emissions trading systems (ETS) have emerged as a crucial mechanism to incentivize companies to invest in low-carbon technologies. Today, 28 ETS programs are in operation globally, covering approximately 17 percent of global emissions. These systems enable governments to gradually decrease emission caps for sectors, creating carbon allowances that are then auctioned. Companies must purchase one allowance for each tonne of CO2 they emit, thereby driving the transition to a more sustainable future.
Notably, the EU ETS, the world’s most established scheme, witnessed a significant increase in average allowance prices, reaching $83 per tonne in 2022, up from $65 in 2021. Similarly, China’s ETS saw the average allowance price rise to $8 in 2022, and California and Quebec’s linked ETS experienced a price increase from $21 to $28 during the same period. These price trends reflect the growing value placed on carbon reduction efforts and the pivotal role that carbon markets play in achieving climate goals.
Recent Developments Shaping the Energy Transition
Around the globe, noteworthy developments are driving the energy transition and paving the way for a sustainable future. Germany’s energy watchdog warns further reductions in gas usage by companies and households are needed to avoid potential shortages in the coming winter. This adjustment is a response to Germany’s reduced dependency on Russian pipeline gas, marking a significant step toward energy security and diversification.
Africa celebrated its largest renewable energy deal to date when Infinity Power acquired a 100 percent stake in wind power platform Lekela Power. With ambitious plans to install and operate 2 gigawatts of new wind power projects by 2025, Infinity Power aims to double its current renewable energy portfolio, making a substantial contribution to the continent’s sustainable development.
Europe is gearing up to boost its carbon dioxide storage capacity through proposed legislation known as the Net Zero Industry Act. This act aims to target a storage capacity of 50 million tonnes of CO2 annually by 2030, a crucial step toward achieving carbon neutrality and combating climate change.
In the maritime sector, the European Union and its member countries have reached a preliminary agreement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by increasing the utilization of renewable fuels on ships. This proactive approach demonstrates the commitment of the maritime industry to reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner and greener future.
China, a global leader in renewable energy deployment, is set to launch a pilot scheme to promote the development of renewable energy in rural areas. Provincial-level governments will identify potential sites for renewable energy projects, with the ambitious target of sourcing about 30 percent of total primary energy consumption from renewable sources. This initiative aims to address energy poverty and promote sustainable development in underserved regions.